Blog 1
Today's lesson will be about the Carbon cycle and the important process it plays on earth to maintain the balance to enable life on earth. Below is an outline of the content covered and an activity sheet outlining the project that will be completed over the next few weeks.
Carbon cycle shows the movement of carbon in elemental and combined states on earth. Diamond and graphite are the elemental forms of carbon and in a combined state, it is found as carbonates in minerals and as carbon dioxide gas in the atmosphere.
Table of Contents
Read on to explore the definition and the steps involved in the carbon cycle. Also learn the various elements of the carbon cycle diagram.
Carbon Cycle Definition
Carbon cycle is the process where carbon compounds are interchanged among the biosphere, geosphere, pedosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of the earth.
Carbon Cycle Steps
Following are the major steps involved in the process of the carbon cycle:
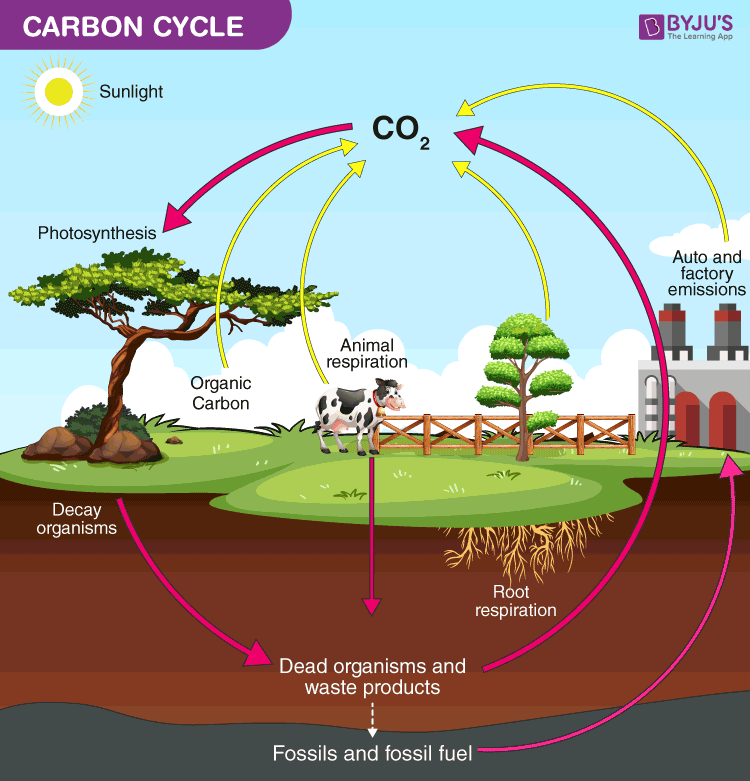
- Carbon present in the atmosphere is absorbed by plants for photosynthesis.
- These plants are then consumed by animals and carbon gets bioaccumulated into their bodies.
- These animals and plants eventually die, and upon decomposing, carbon is released back into the atmosphere.
- Some of the carbon that is not released back into the atmosphere eventually become fossil fuels.
- These fossil fuels are then used for man-made activities, which pump more carbon back into the atmosphere.
Also Read: Biogeochemical Cycles
Carbon Cycle Diagram
The carbon cycle diagram below elaborates the flow of carbon along different paths.
Carbon Cycle on Land
Carbon in the atmosphere is present in the form of carbon dioxide. Carbon enters the atmosphere through natural processes such as respiration and industrial applications such as burning fossil fuels. The process of photosynthesis involves the absorption of CO2 by plants to produce carbohydrates. The equation is as follows:
CO2 + H2O + energy → (CH2O)n +O2
Carbon compounds are passed along the food chain from the producers to consumers. The majority of the carbon exists in the body in the form of carbon dioxide through respiration. The role of decomposers is to eat the dead organism and return the carbon from their body back into the atmosphere. The equation for this process is:
(CH2O)n +O2 → CO2 + H2O
Oceanic Carbon Cycle
This is essentially a carbon cycle but in the sea. Ecologically, oceans take in more carbon than it gives out. Hence, it is called a “carbon sink.” Marine animals convert carbon to calcium carbonate and this forms the raw building materials require to create hard shells, similar to the ones found in clams and oysters.
When organisms with calcium carbonate shells die, their body decomposes, leaving behind their hard shells. These accumulate on the seafloor and are eventually broken down by the waves and compacted under enormous pressure, forming limestone.
When these limestone rocks are exposed to air, they get weathered and the carbon is released back into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
Importance of Carbon Cycle
Even though carbon dioxide is found in small traces in the atmosphere, it plays a vital role in balancing the energy and traps the long-wave radiations from the sun. Therefore, it acts like a blanket over the planet. If the carbon cycle is disturbed it will result in serious consequences such as climatic changes and global warming.
Carbon is an integral component of every life form on earth. From proteins and lipids to even our DNA. Furthermore, all known life on earth is based on carbon. Hence, the carbon cycle, along with the nitrogen cycle and oxygen cycle, plays a vital role in the existence of life on earth.
Key Points on Carbon Cycle
- Carbon cycle explains the movement of carbon between the earth’s biosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere.
- Carbon is an important element of life.
- Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is taken up by green plants and other photosynthetic organisms and is converted into organic molecules that travel through the food chain. Carbon atoms are then released as carbon dioxide when organisms respire.
- The formation of fossil fuels and sedimentary rocks contributes to the carbon cycle for very long periods.
- The carbon cycle is associated with the availability of other compounds as well.
Comments
Post a Comment